In-depth Analysis: Principles, Applications, and Selection Key Points of Laser Distance Sensors and Laser Displacement Sensors
The Rise and Development Trends of Optical Measurement Sensors
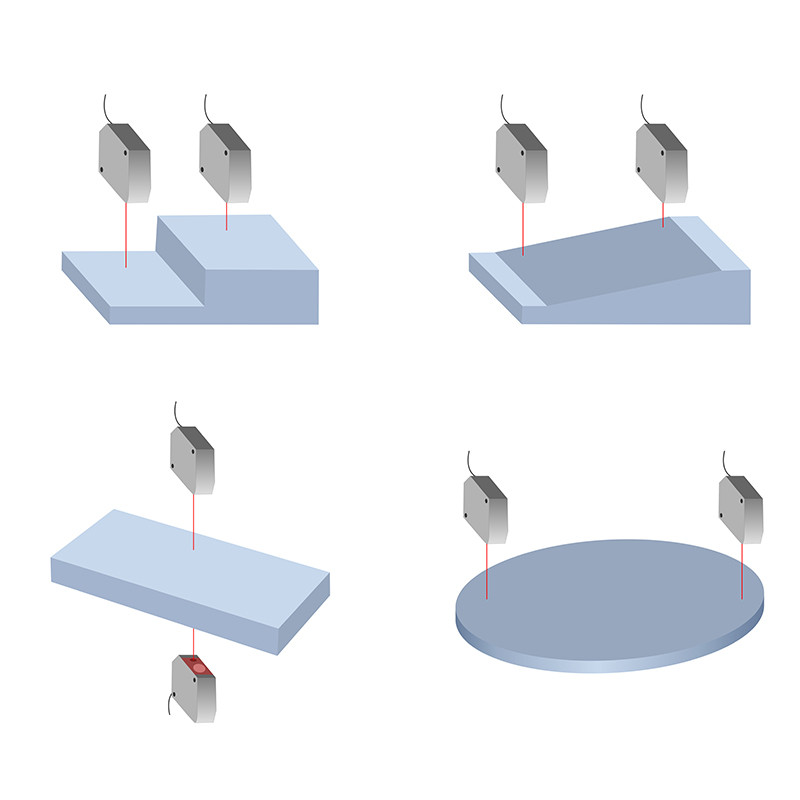
The Fundamentals and Classification of Laser Distance Measurement Technology
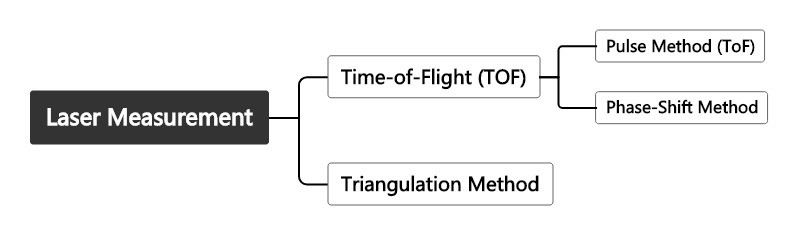
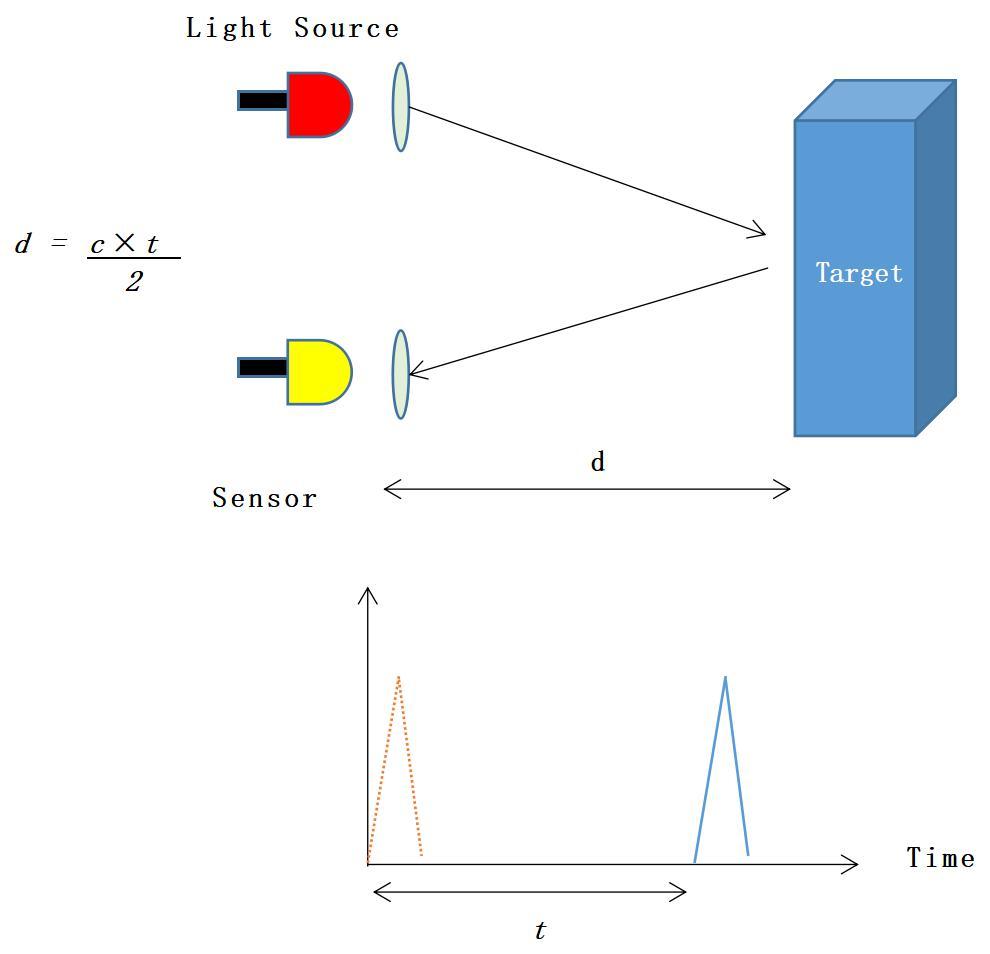
Pulse Method (ToF): The Ideal Choice for Long-Distance and Large-Scale Measurement
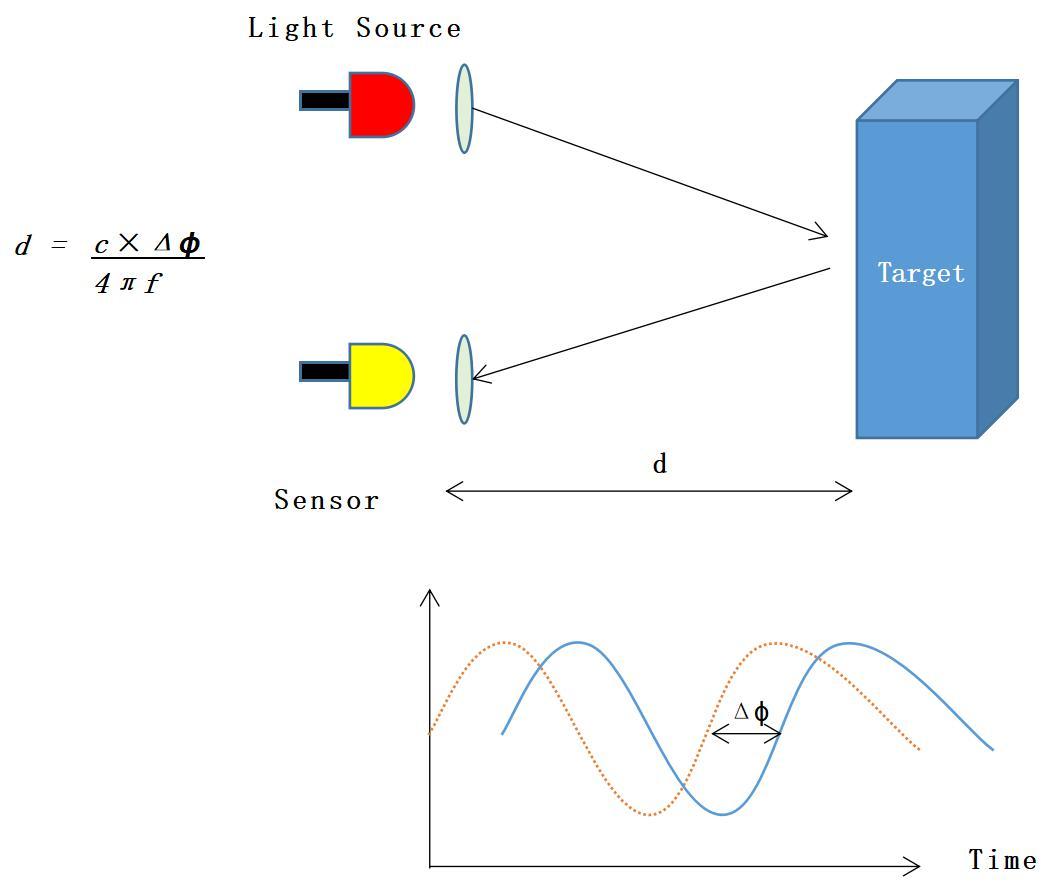
Phase-Shift Method: Reliable Technology for Medium and Short-Distance High-Precision Measurement
Triangulation Method: A Precision Tool for Ultra-Short-Distance Measurement
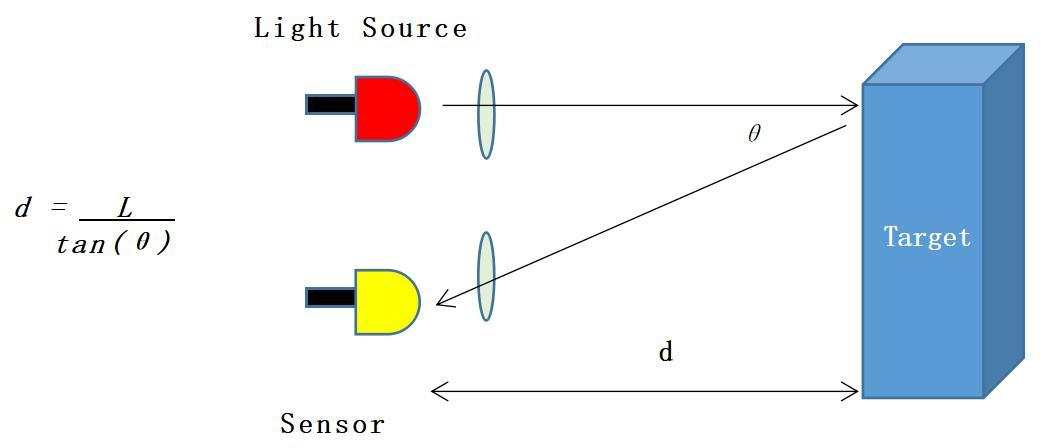
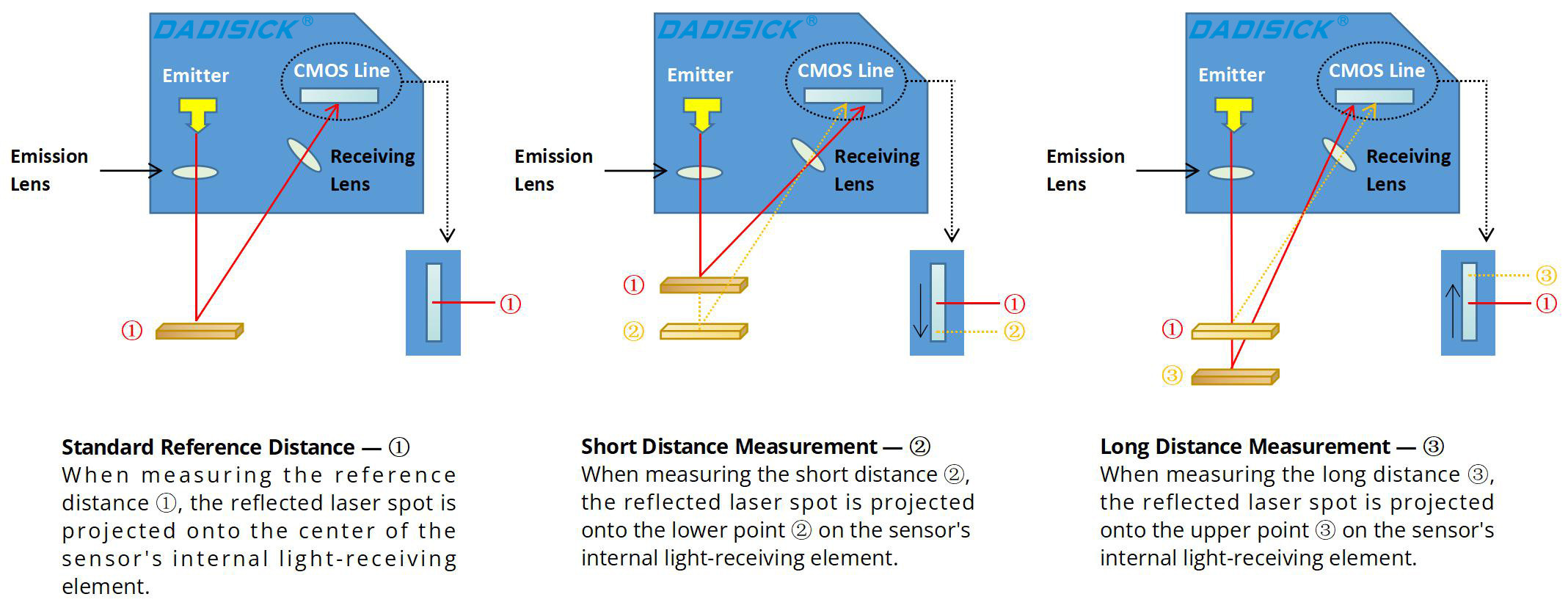
Selection Key Points of Laser Distance Sensors and Displacement Sensors
Product | Laser Displacement Sensor | Laser Distance Sensor | ||
Series | GFL-G Series | GFL-Z Series | GFL-Y Series | DA-Y & DB-Y Series |
Measurement technology | Triangulation Method | Time of Flight: Phase-Shift Method | ||
Measurement Range | 30 mm (±4); 50 mm (±10); 85 mm (±20); 120 mm (±60); 250 mm (±150) | 30 mm (±5); 50 mm (±15); 100 mm (±35); 200 mm (±80); 400 mm (±200); | 0.1 - 1 m; 0.1 - 2 m; 0.1 - 5 m; 0.1 - 10 m; 0.1 - 20 m; 0.1 - 50 m; | 0.2 - 10 m; 0.2 - 20 m; 0.2 - 30 m; 0.2 - 50 m; 0.2 - 100 m; |
Resolution | Min. 2 μm; Max. 75 μm | — | 1 mm | 1 mm |
Repeatability | — | Min. 10 μm, Max; 800 μm | — | — |
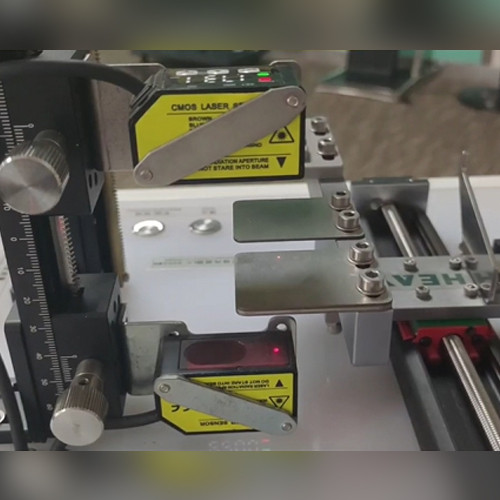
Laser type | Class ll, Wavelength: 655 nm | Class ll, Wavelength: 655 nm | Class ll, Wavelength: 655+10 nm | Class ll, Wavelength: 660±15 nm |
Protection Rating: | IP64 | IP60 | IP67 | IP67 |
Supported Interfaces | RS485 / Switch Output / Analog (4 to 20 mA or 0 to 5 V) | RS485 / Switch Output / Analog (4 to 20 mA or 0 to 5 V) | RS232 / RS485 / Switch Output / Analog (4 to 20 mA or 0 to 5 V) | |
Function | Mainly used to measure small displacement changes or surface position deviations of an object. It typically focuses on high-precision dynamic or static displacement relative to a reference point (e.g., vibration, deformation, flatness, etc.). | Focuses on measuring the absolute distance between two points (e.g., the straight-line distance from the sensor to an object). It is suitable for medium- to long-range static or slow-moving dynamic scenarios. | ||
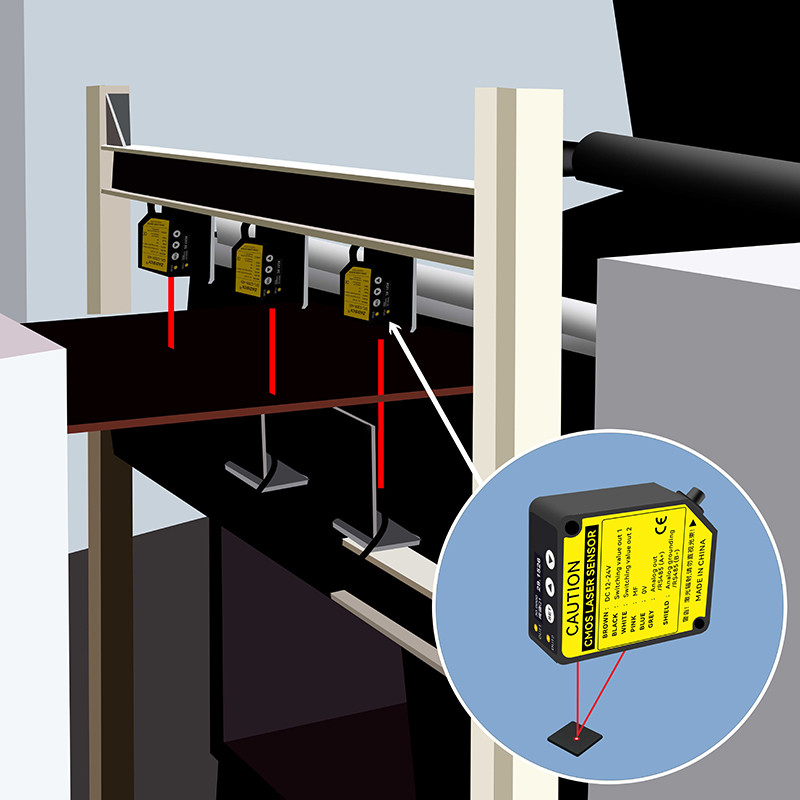
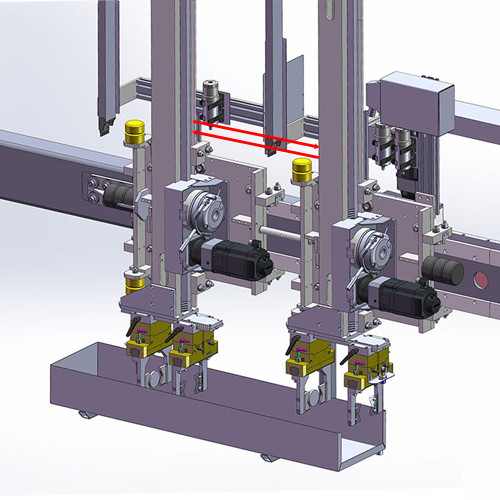
Typical Applications | Industrial Inspection: • Measurement of component thickness, flatness, and roundness (e.g., bearings, chips). • Real-time quality control on production lines (e.g., detecting product dimensional deviations). | Surveying and Construction: • Terrain mapping, building height measurement. • Spatial distance calibration in indoor renovations. | ||
Dynamic Monitoring: • Mechanical vibration analysis (e.g., operational status of motors, turbines). • Material deformation testing (e.g., micro-movements in bridges and building structures). | Robotics and Autonomous Navigation: • Obstacle avoidance and navigation (e.g., robotic vacuum cleaners, drones). • Safety distance monitoring between vehicles. | |||
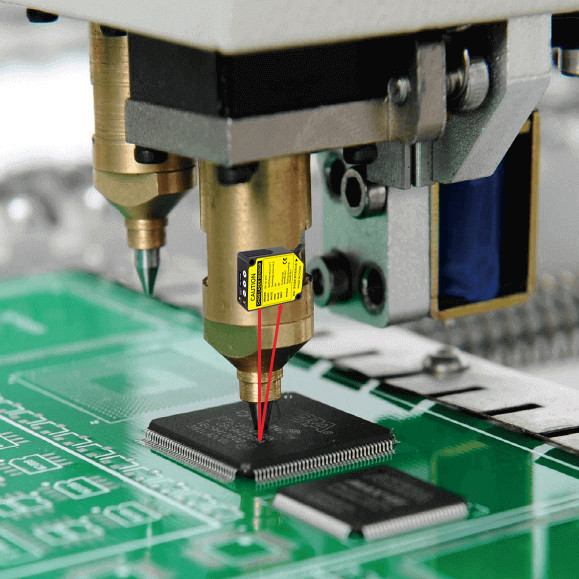
Precision Machining: • Monitoring tool wear in machine tools. • 3D scanning and surface profile reconstruction. | Security and Monitoring: • Perimeter protection (detecting intruder distance). • Speed measurement in sports events (e.g., athletics, racing). | |||
Measurement Target | Relative displacement changes (minute, dynamic) | Absolute distance (static or slow-moving dynamic) | ||
Accuracy | Micrometer to nanometer level | Millimeter to centimeter level | ||
Measurement Range | Short (typically a few millimeters to several meters) | Large (several meters to kilometers) | ||
Typical Scenarios | Industrial inspection, vibration analysis | Surveying, robotic navigation, security | ||