Unlocking Precision: What Is a Laser Displacement Sensor? (Principle & Types) – DADISICK's Expert Guide
What Is a Laser Displacement Sensor? (Principle & Types)

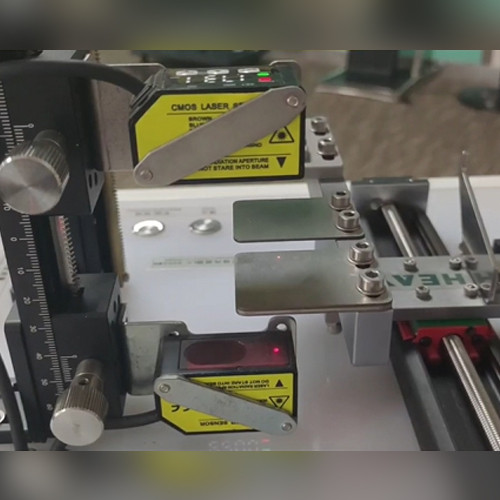
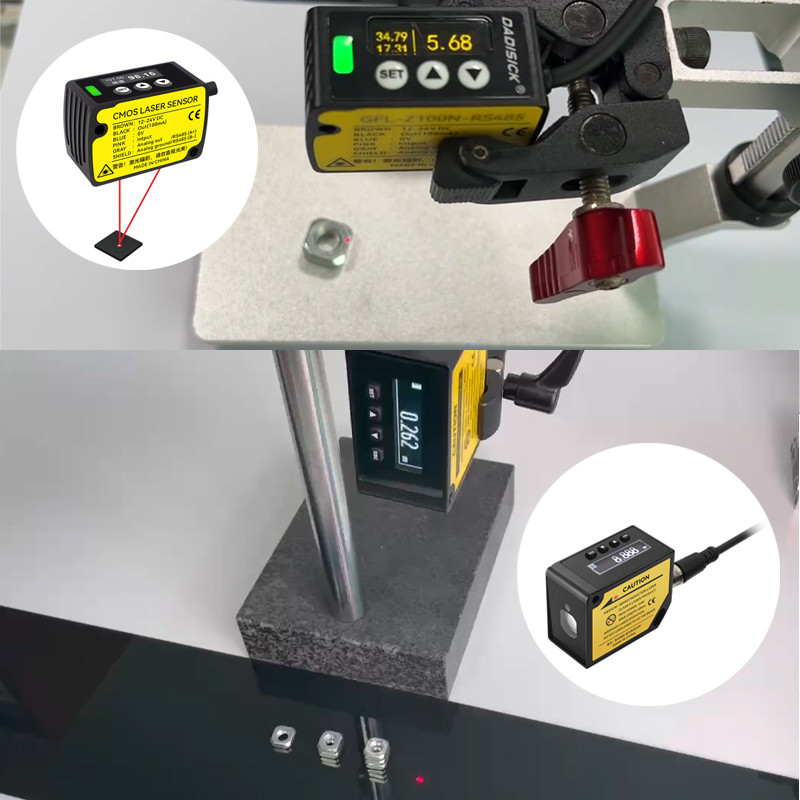
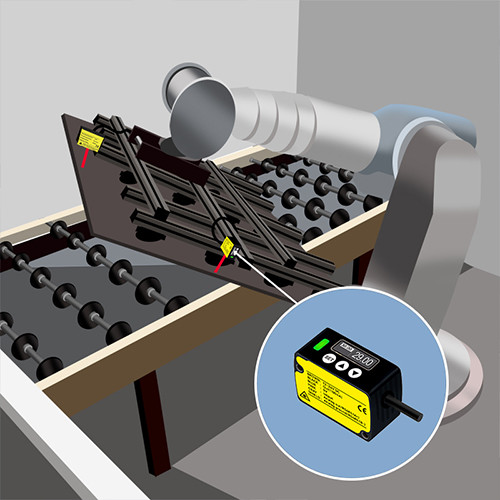
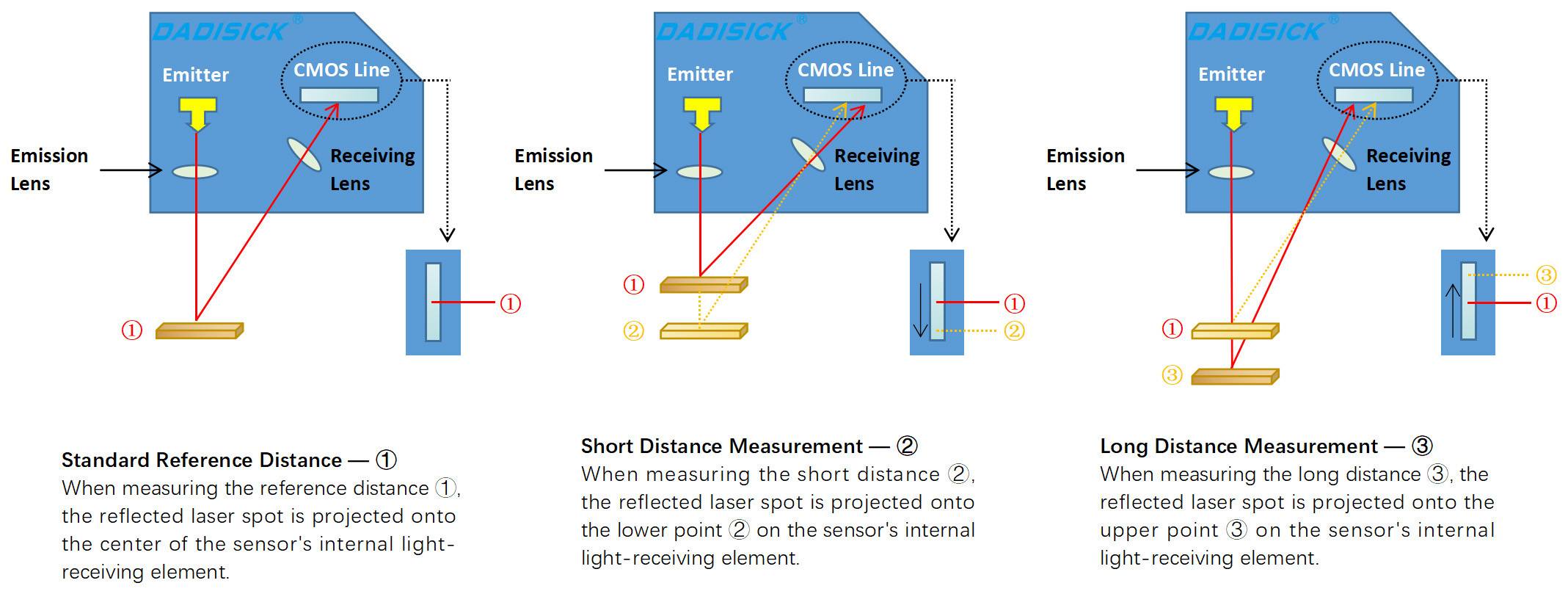
Laser Displacement Sensor Working
Laser Triangulation
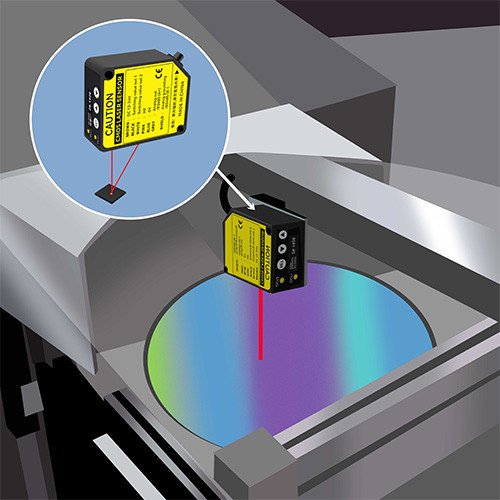
Confocal Principle
Types of Laser Displacement Sensors
| Sensor Type | Measurement Principle | Strengths | ||
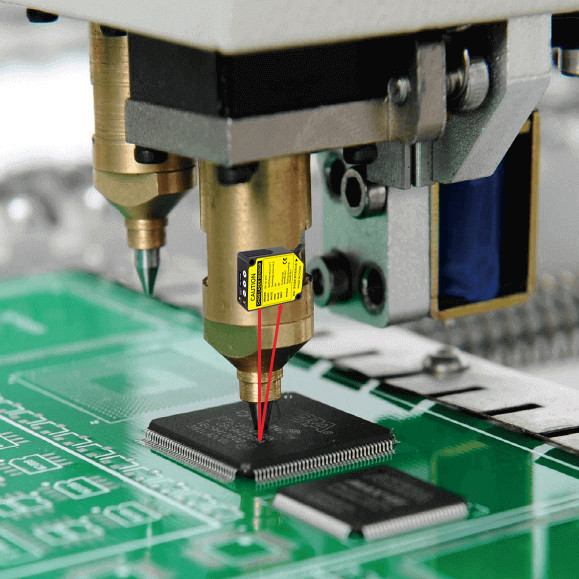
| 1D Triangulation | Single-point spot & PSD/CMOS | High speed, compact heads, µm accuracy | ||
| Multi-Color Confocal | Axial chromatic focus variation | Stable on glossy/transparent surfaces, robust | ||
| Spectral Interference | Interferometry using spectral analysis | Ultra-high resolution, limited range | ||
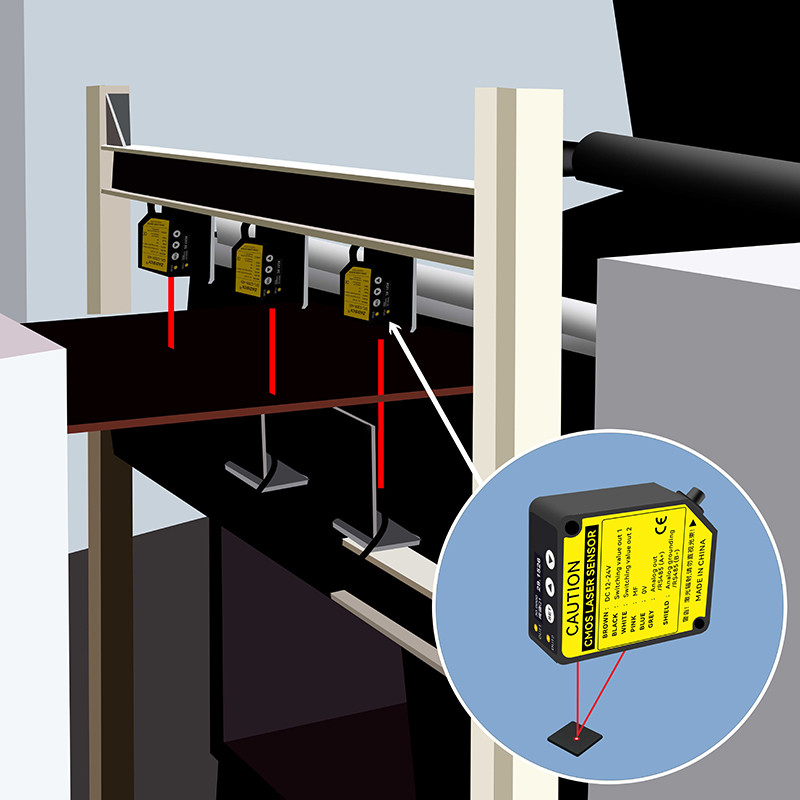
2D/3D Laser Profiler | Line or plane scanning | Full cross-section or surface mapping | ||
•Multi-Color Confocal: Best for transparent or highly reflective materials where triangulation struggles.
•Spectral Interference: Provides nm-level resolution for very short ranges (often <1 mm).
•Laser Profilers (2D/3D): Build line-scan or area-scan profiles for complex 3D inspections.
Why Choose a Laser Displacement Sensor?
•Fast Response: Sampling rates up to hundreds of kHz for real-time control on high-speed lines.
•Versatile Integration: Multiple output protocols (analog, NPN/PNP switch, RS-485, Ethernet, IO-Link) and compact heads fit tight spaces and robot mounts
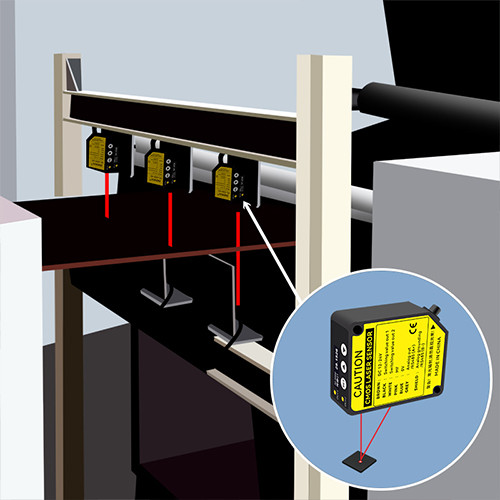
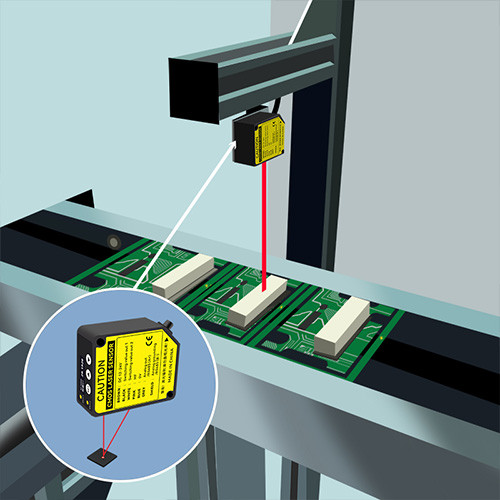
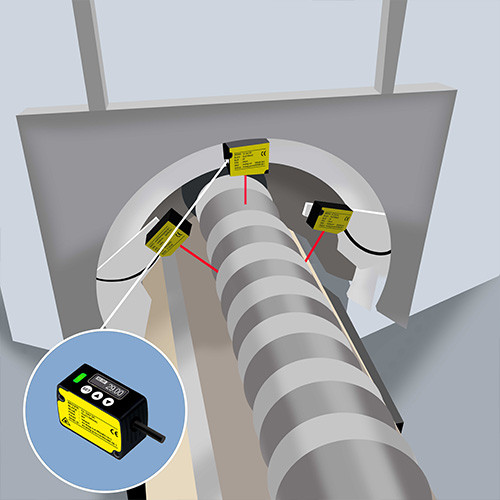
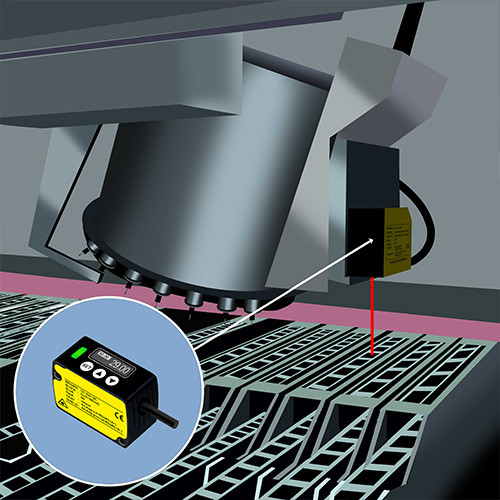
Find the right Laser Measurement Sensor for Your Application